Origins of the Twenty-One Gun Salute
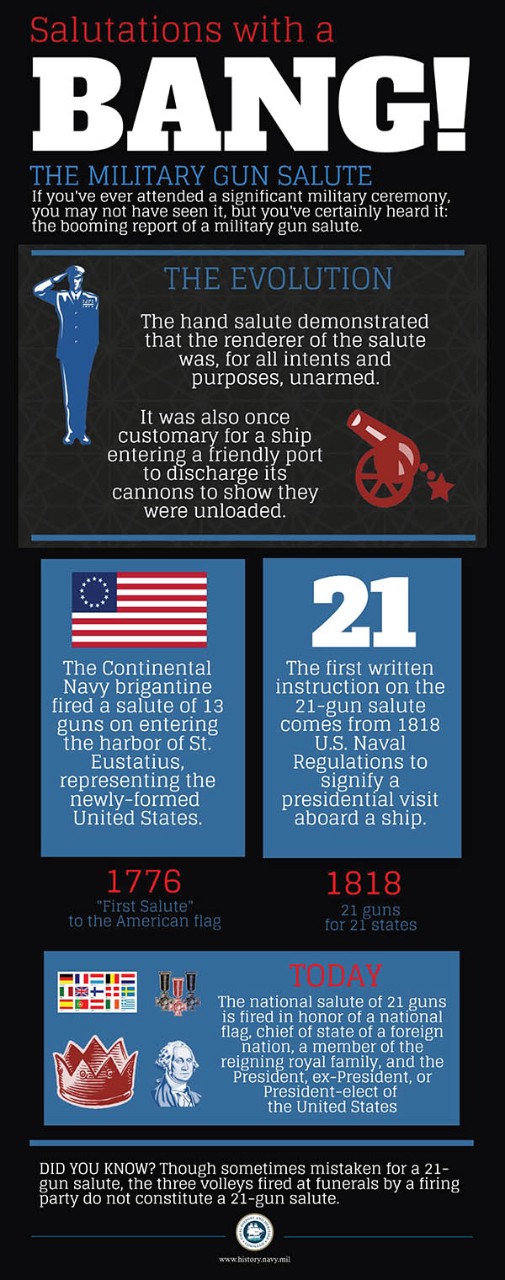
The practice of firing gun salutes has existed for centuries. Early warriors demonstrated peaceful intentions by placing their weapons in a position that rendered them ineffective. Starting in the fourteenth century, as firearms and cannons that contained only one projectile came into use, discharging the projectile before entering a friendly port demonstrated that they were unloaded.
The rendering of gun salutes in odd numbers may be traced to the superstition that odd numbers were considered lucky. Seven, for example, was believed by early civilizations to have mystical powers. Forts ashore, which could store gunpowder more readily and in greater quantity than on board ship, would sometimes fire three shots for each shot fired afloat. Salutes with an even number of guns came to signify that the captain or ship master had died on the voyage.
For many years, the number of guns fired for various purposes differed from country to country. By 1730, the Royal Navy was prescribing twenty-one guns for certain anniversary dates, although this was not mandatory as a salute to the royal family until later in the eighteenth century.
Several famous incidents involving gun salutes took place during the American Revolution. On 16 November 1776, the Continental Navy brigantine Andrew Doria, Captain Isaiah Robinson, fired a salute of 13 guns on entering the harbor of St. Eustatius in the West Indies (some accounts give 11 as the number). A few minutes later, the salute was returned by 9 (or 11) guns by order of the Dutch governor of the island. At the time, a 13 gun salute would have represented the 13 newly formed United States; the customary salute rendered to a republic at that time was 9 guns. This has been called the “first salute” to the American flag. About three weeks before, however, an American schooner had her colors saluted at the Danish island of St. Croix. The flag flown by Andrew Doria and the unnamed American schooner in 1776 was not the Stars and Stripes, which had not yet been adopted. Rather, it was the Grand Union flag, consisting of thirteen alternating red and white stripes with the British Jack in the union.
The first official salute by a foreign nation to the Stars and Stripes took place on 14 February 1778, when the Continental Navy ship Ranger, Captain John Paul Jones, fired 13 guns and received 9 in return from the French fleet anchored in Quiberon Bay, France.
The U.S. Navy regulations for 1818 were the first to prescribe a specific manner for rendering gun salutes (although gun salutes were in use before the regulations were written down). Those regulations required that “When the President shall visit a ship of the United States’ Navy, he is to be saluted with 21 guns.” It may be noted that twenty-one was the number of states in the Union at that time. For a time thereafter it became customary to offer a salute of one gun for each state in the Union, although in practice there was a great deal of variation in the number of guns actually used in a salute.
In addition to salutes offered to the President and heads of state, it was also a tradition in the U.S. Navy to render a “national salute” on 22 February (Washington's Birthday) and 4 July (the anniversary of the Declaration of Independence).
A 21 gun salute for the President and heads of state, Washington's Birthday, and the Fourth of July became the standard in the United States Navy with the issuance of new regulations on 24 May 1842. Those regulations laid out the specifics:
“When the President of the United States shall visit a vessel of the navy, he shall be received with the following honors: The yards shall be manned, all the officers shall be on deck in full uniform, the full guard shall be paraded and present arms, the music shall play a march, and a salute of twenty-one guns shall be fired. He shall receive the same honors when he leaves the ship.”
“Upon the anniversary of the Declaration of Independence of the United States, the colors shall be hoisted at sunrise, and all the vessels of the navy shall, when in port, be dressed, and so continue until the colors are hauled down at sunset, if the state of the weather and other circumstances will allow it. At sunrise, at meridian, and at sunset, a salute of twenty-one guns shall be fired from every vessel in commission mounting six guns and upwards.”
“On the twenty-second day of February, the anniversary of the birth of Washington, a salute of twenty-one guns shall be fired at meridian from every vessel of the navy in commission mounting six guns and upwards.”
Today, the national salute of twenty-one guns is fired in honor of a national flag, the sovereign or chief of state of a foreign nation, a member of a reigning royal family, and the President, former Presidents, and the President-elect of the United States. It is also fired at noon of the day of the funeral of a President, former President, or President-elect, on Washington’s Birthday, Presidents Day, and the Fourth of July. On Memorial Day, a salute of twenty-one minute guns is fired at noon while the flag is flown at half mast.
Sources:
Gardner W. Allen, A Naval History of the American Revolution 1: 159-60 (Boston: Houghton Mifflin, 1913).
Naval Documents of the American Revolution 7 (Washington, D.C.: Naval History Division, Dept. of the Navy, 1976).
Naval Regulations, Issued by Command of the President of the United States of America, January 25, 1802 (Annapolis, Md.: Naval Institute Press, 1970).
Rules, Regulations, and Instructions for the Naval Service of the United States... (Washington, D.C.: E. De Kraft, 1818).
Rules and Regulations for the Navy..., 27th Cong. 3d Sess., H. Doc. 148 (Washington, D.C., 1843).
21 May 1996