Preston III (Destroyer No. 19)
1909-1919
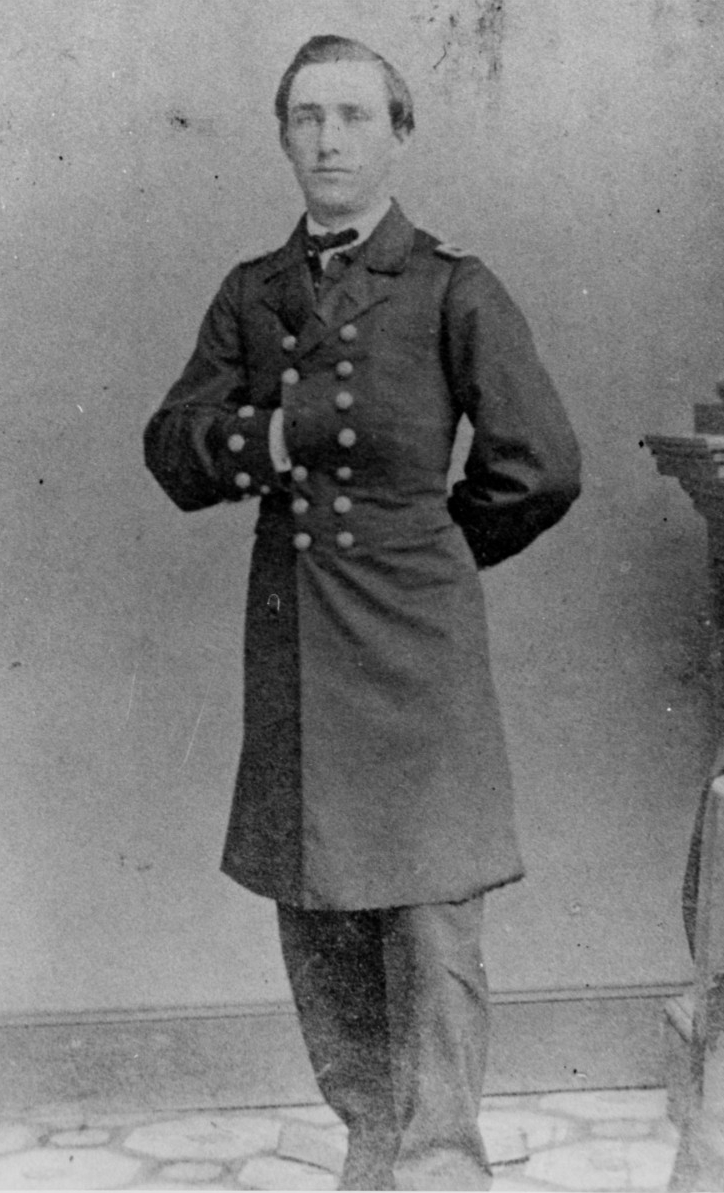

Samuel W. Preston was born in the United Province of Canada, a British colony, on 5 April 1841. His family eventually moved to Illinois, and on 4 October 1858 he was appointed midshipman from that state and remained at the Naval Academy as the country descended into civil war. The war began in earnest in April 1861 and on 9 May 1861 Midshipman Preston graduated early with the second class at the Naval Academy, ranked first among his peers, after which the Commandant of Midshipmen assigned him to the executive department.
Appointed acting-master on 4 October 1861, Preston served in the South Atlantic Blockading Squadron as Flag Officer Samuel DuPont’s flag lieutenant and aide, working tirelessly and making an indelible impression on his commander. DuPont commended him for his actions at the November 1861 Battle of Port Royal where he flawlessly arranged the squadron commander’s signal flags, relaying important orders for an intricately planned operation. Port Royal fell to the federal forces. After Preston received promotion to lieutenant on 1 August 1862, the admiral petitioned Washington to grant the young officer a much needed break from the squadron. He wrote to Assistant Secretary of the Navy Gustavus V. Fox that Preston had “Overworked himself, and if I were to express to you the amount of his services in this fleet… you could hardly credit it… such men are born about once in a quarter century.”
By October 1862, Preston returned to the squadron, and remained with the admiral when the ironclads of the southern blockading squadron engaged the defenses of Charleston, S.C. on 7 April 1863. The young officer participated in the battle on board the ironclad New Ironsides. Again Preston impressed his commander by arranging a special code book of signals and serving on the gun deck battery. The attack, however, proved unsuccessful. On 15 May 1863, the British schooner Wonder attempted to run the blockade. A federal lightship out of Port Royal, S.C., informed Rear Adm. DuPont that the schooner had earlier requested a pilot familiar with rebel-held Savannah. The admiral dispatched Preston to the side wheel steamer Daffodil to overtake the vessel. Locating the schooner in the dark, he boarded her and determined that her master intended to trade with the Confederacy, after which the energetic officer confiscated the ship along with her cargo and sent the crew to New York.
When Rear Adm. Dahlgren assumed command of the squadron, Preston remained as flag lieutenant. Throughout the summer of 1863, the South Atlantic Blockading Squadron focused on the islands key to capturing Charleston Harbor. Rear Adm. Dahlgren thanked him in his general orders for his actions during the unsuccessful 11 July 1863 attack on the Morris Island bastion of Fort Wagner. Following the second ill-fated assault on 18 July, Preston walked through the dead and wounded and approached the fort under a flag of truce, offering to evacuate the Union wounded to the ships off shore, a request the rebels denied. On 30 July, Rear Adm. Dahlgren sent Lt. Preston, suffering from an unnamed ailment, to Washington to recuperate. While in the capital, Lt. Preston spoke with Assistant Secretary of the Navy Fox and President Abraham Lincoln, passing on Dahlgren’s complaints about the Army force cooperating with the Navy in South Carolina.
In late August the federal squadron severely damaged Fort Sumter. A flying splinter severely injured Rear Adm. Dahlgren’s fleet captain during the bombardment, and the admiral placed Preston in that advanced role. Following the reduction of Sumter, the Union made a third attempt to take the stubborn Fort Wagner. Preston proved extremely active as Rear Adm. Dahlgren coordinated with Army Maj. Gen. Quincy Gillmore during the investment of the battery. He passed messages between the often bickering commanding officers and provided intelligence and situation reports to the admiral. The combination of the bombardment of the fort with the approaching army trench lines helped convince the garrison to evacuate on 7 September.
With Fort Wagner and Morris Island occupied, Rear Adm. Dahlgren targeted what remained of Fort Sumter and called for volunteers to launch an assault on the island. Preston answered the call, specifically requesting to participate in the assault. Despite reservations toward putting his irreplaceable aide in harm’s way Rear Adm. Dahlgren named him commander of the third division. At 1:00 a.m. on 9 September 1863 boats shoved off and approached the fort. Unknown to the Federals, the rebel garrison had deciphered the signals exchanged between the union forces and anticipated the coming attack. The naval force rushed onto the beach under the damaged walls of the fort. Confederate fire immediately pinned them down against the fortress walls. Preston and the fellow raiders watched helplessly while the garrison disabled their boats with bricks and grenades. The defenders captured Preston along with 125 men, and took him to Columbia, S.C., where he was imprisoned at the Richland County Jail.
Located in the capital of South Carolina, the jail housed 132 union officers and 99 enlisted men by the time Preston was released. Adding the Federal prisoners to an already large prison population led to overcrowding. The highest ranking union officer in the jail requested additional funds in May 1864 so that the naval officers, including Lt. Preston, could obtain supplies. While imprisoned, he reestablished a strong friendship with fellow prisoner and Naval Academy classmate Lt. Benjamin H. Porter. The two would continue to serve together throughout the war. The South Atlantic Blockading Squadron sorely missed his aide’s services, Rear Adm. Dahlgren explained oversights by the officer’s absence on multiple occasions which “necessarily deranged all the business of my command very much.” In the autumn of 1864, Preston returned to the Navy in a prisoner exchange.
On his return, Preston immediately applied for active service and the Navy assigned him to the Northern Atlantic Blockading Squadron as flag lieutenant of Rear Adm. David Dixon Porter. By the time he reported to the flagship Powhatan, the Union had captured or isolated all but one of the Confederacy’s major ports. Wilmington, N.C. alone stood defiant against the Federal blockade. Fort Fisher, known as “The Gibraltar of the South” served as the primary obstacle preventing naval forces from ascending the Cape Fear River and shutting down that crucial hub, as her sand and soil walls absorbed bombardment while her powerful battery kept the federal vessels at a safe distance. The landward facing works proved equally fearful, with interlocking fields of fire commanding difficult approaches over open sand and swamp. Secretary of the Navy Gideon Welles placed Rear Adm. Porter in command of naval operations against the fort.
Rear Adm. Porter’s Army counterpart, Maj. Gen. Benjamin Butler, formulated a daring plan to weaken the fort before assault, proposing that the Navy load an old vessel with gunpowder and beach her near the fort. The fleeing crew would light a fuse. Following the ensuing explosion, the army would storm the damaged fort and force the stunned garrison to surrender. The plan gained influential support despite ordnance experts doubting its feasibility. The squadron transformed the flat-bottomed steamer Louisiana into a floating bomb carrying 215 tons of gunpowder and camouflaged her to look like a blockade runner. Preston volunteered for the hazardous mission as second-in-command on board Louisiana. The officers knew that there was a high probability that the gambit could end in disaster. In addition to the inherent danger of stoking a fire on a ship packed with explosives, Preston and the ship’s commanding officer made a pact to sacrifice themselves by blowing the vessel up if boarded. Rear Adm. Porter later described the mission as “the most perilous adventure that was perhaps ever undertaken.” On 18 December 1864, Louisiana made a first approach to Fort Fisher but was recalled when Maj. Gen. Butler claimed the weather was unfavorable for the assault. The Federals postponed the attack and the army transports put into port to coal and resupply.
Rear Adm. Porter decided to deploy Louisiana in the Army’s absence. On the night of 23 December 1864, the side-wheel steamer Wilderness towed the explosive laden vessel toward the fort. Five-hundred yards from shore, Wilderness cut the tow line and Louisiana fired her engine. After closing on shore, the vessel dropped anchor, dismissed the crew, and Lt. Preston along with two fellow officers primed and set the fuses on the vessel. The three lit a fire as a fail-safe before abandoning ship. Preston and the officers reached Wilderness safely. At 1:46 a.m. on Christmas Eve morning, Louisiana detonated in a column of flame and smoke that lit the waters off of Fort Fisher. Unfortunately, the spectacular blast caused no damage to the position, the officers having beached the vessel further than intended from the fort. The detonating system also malfunctioned, diminishing the power of the blast. Nevertheless, Rear Adm. Porter commended them for their bravery, telling the Secretary of the Navy that they deserved promotion.
An intense two day bombardment followed while the Army returned off shore. On Christmas Day 1864 an army force landed and skirmished with Confederate forces. Ultimately the ground forces determined that the fort was too formidable for assault. Maj. Gen. Butler called off the operation due to the fortress strength and approaching rebel reinforcements. The army departed Cape Fear, leaving Lt. Preston to rage against the “disgraceful conduct of the shrewd political trickster and military imbecile who abandoned all the advantages in our late attack.”
Gen. Ulysses S. Grant provided Lt. Preston and the Navy a second chance to take Fort Fisher one month later. The General wanted to take the city as means to support Gen. William Tecumseh Sherman’s proposed march from Georgia to Virginia. He dispatched another army force, this time under Bvt. Maj. Gen. Alfred Terry to cooperate with the navy, the latter force again under Rear Adm. Porter.
Arriving on the morning of 13 January 1865, the Army landed several miles north of Fort Fisher. They avoided a cautious Confederate force and marched down the peninsula, setting up defensive lines facing north that cut off the garrison from landward communications and reinforcements. Meanwhile the federal fleet began bombarding the fortress, a process that lasted over two days, knocking out guns one at a time with furious cascades of shell. As the sun rose over the sands of Fort Fisher on 15 January, the stage was set for the final assault.
The federal commanders agreed upon a joint Army-Navy assault. Rear Adm. Porter laid out the naval force’s orders. After the Army initiated the assault on the landward side, a force of marines and Navy volunteers “armed with cutlasses, well sharpened, and with revolvers,” would “board the fort on the run in a seaman-like way,” at the seaward fortifications. On the morning of 15 January 2, 261 sailors landed on the beach to the northeast of the fort. Lt. Preston was among the first volunteers and played an integral part of Rear Adm. Porter’s plan. In order to quiet the remaining guns, the admiral planned to deploy marine marksmen in covered positions within firing range of the parapet. Rear Adm. Porter ordered Lt. Preston to lead ten sailors in an advance party to dig rifle pits. On the morning of 15 January 1865 his men furiously burrowed into the sand for hours. Armed only with shovels they pushed forward over the exposed sand through “a brisk fire of grape and musketry from the fort.” The small party finished its final line only 175 yards from the rebel fortifications.
After the final shovel emptied its contents and 300 marines occupied the positions, the lieutenant reported to the commander of the assault, Fleet-Capt. Kidder Breese, who sent him on an errand to the rear. The tars waited, lying prone one-half mile from the fort as marksmen’s bullets and misaimed federal shells landed sporadically in their ranks. Rear Adm. Porter ordered the naval officers to wait for the Army assault before initiating their own assault. Due to miscommunication, the navy believed the attack would occur an hour before the army, forcing the sailors to endure morale sapping and fatigue inducing afternoon. By 3:00 p.m., Lt. Preston had rejoined the force as they crept along the beach to 600 yards from the fortress. Beside the lieutenant was his old friend Lt. Benjamin Porter, now the captain of the admiral’s flagship Malvern. The two took places at the head of the extreme left of the first column. Finally, at 3:25 p.m., the fleet ceased their bombardment and scores of steam whistles pierced the quiet, signaling the attack.
Sailors and marines leapt up and took their first strides in the soft sand. The admiral’s orders instructed the force to wait for the army’s attack but they surged ahead impetuously from the outset. The first division, Lt. Preston and Lt. Porter in the lead, surged down the narrow beach as the confederate garrison, having weathered the bombardment in secure bombproofs, poured into their positions on the parapet. Col. William Lamb, the commander of the fort, deployed the strength of his force at the Northeast bastion, directly opposing the naval assault. Canister, grape and shell raked the compact formation along the length of the beach and tore into its exposed flank. Worsening the already grave outlook, confused orders led the marines providing covering fire to leave their rifle pits prior to the assault and join the column.
The column advanced only one-hundred yards down the beach before the first ranks dove into the sand, shocked by the severity of the murderous fire. Lt. Preston and the officers continued on, beckoning their men to follow them. Federals fell dead and wounded in ever-increasing numbers as they met the storm of shot. At 300 yards, half-way to the fort, the majority of the force again dropped into the sand in anticipation of the report of rebel artillery. Most chose the limited shelter of the exposed sand to continuing the mad dash. The officers pushed forward ahead of the 150-200 disorganized sailors and marines left on their feet.
While passing under the guns at the bastion the attackers soon approached another obstacle, a palisade that stood between the onrushing tars and leathernecks and their objective at the sea face. Here, the rebels delivered the coup de grâce. As the Federal column advanced Col. Lamb withheld the fire of the scores of Carolinians along the parapet. As they awaited the Federal ranks Lamb instructed his men to pick out the officers -- easily identified by their ornate uniforms -- then at point blank range ordered his riflemen to fire.
Well aimed volleys repeatedly tore through the Union ranks. Singularly focused on the objective, Lt. Preston likely did not notice his friend Lt. Porter fall dead, shot in the chest. Seconds later Lt. Preston ran into view of another close friend, classmate, and former shipmate, Lt. Roswell Lamson, commanding officer of the steamer Gettysburg, who later recalled: “When near the palisades, Mr. Preston was struck in the left thigh or groin, the femoral artery being severed.” Lamson watched helplessly as his friend pitched face first into the sand. A bluejacket stopped to assist the flag lieutenant, only to fall dead on top of the wounded officer. A second sailor freed Lt. Preston who rolled onto his back as the broken mass of survivors fled on all sides. Lamson, shot through the arm, attempted to crawl to the assistance of his comrade, but a wounded sailor waved him off, telling him that Preston was dead. Left pinned against the walls of Fort Fisher until nightfall, Lamson mourned his comrade “not only as a dear friend lost, but as a loss to the service of the most superior young officer I have ever seen in it.” Preston was 23 years of age.
Preston’s sacrifice and those of comrades had not been in vain, for while much of the garrison was defending the northeast bastion, the army poured into the fort from the land face, eventually capturing the stronghold on the night of 15 January 1865. The fall of the fort effectively isolated Wilmington from sea traffic and the Confederacy to their last major lifeline.
Reflecting on the battle, Fleet-Capt. Breese recalled how Lt. Preston “fell among the foremost at the front, as he had lived, the thorough embodiment of a United States naval officer.” Of Preston and Porter he stated, “Two more noble spirits the world never saw, nor had the Navy ever two more intrepid men. Young, talented, and handsome, the bravest of the brave, pure in their lives, surely their names deserve something more than passing mention and are worthy to be handed down in posterity with the greatest and best of naval heroes.”
Preston’s remains were originally placed on board Malvern, and later transferred to Santiago de Cuba to be transported to Hampton Roads, thence to Annapolis, where they lie buried in the U.S. Naval Academy Cemetery.
(Destroyer No. 19: displacement 700 (standard); length 293'10", beam 26'0", draft 8'0"; speed 29.18 knots; complement 88; armament 5 3-inch guns, 6 18-inch torpedo tubes; class Smith)
The first Preston (Destroyer No. 19) was laid down on 28 April 1908 at Camden, N.J. by the New York Shipbuilding Co.; launched on 14 July 1909; sponsored by Miss Katherine Magoun; delivered to the Navy on 21 December 1909 at the Philadelphia Navy Yard, and commissioned on 24 December 1909, Lt. Cmdr. George C. Day in command.
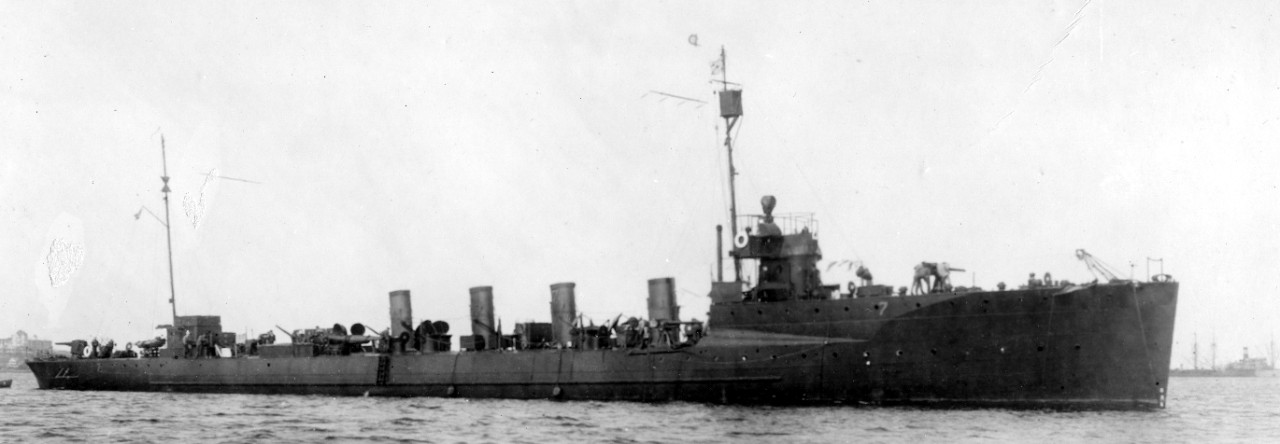
Assigned to the Atlantic Squadron, Preston operated along the east coast and in the Caribbean from 1910 until 1916 participating in torpedo exercises, fleet maneuvers, and coastal patrol. Steaming through a storm in January 1912 the vessel was tossed about and much of the equipment stowed above deck was either lost or damaged. In 1916 she conducted neutrality patrols and guarded interned belligerent vessels in the harbor at San Juan, Puerto Rico. When the interned German steamer Odenwald grounded in the harbor as a result of a hurricane (22 August 1916), Preston made four attempts to float the vessel by towing her, only succeeding after steaming on four boilers at 21 knots. She attempted to tow the American steamer J. Homes Burdsell after she grounded at the entrance of San Juan harbor but was unsuccessful.
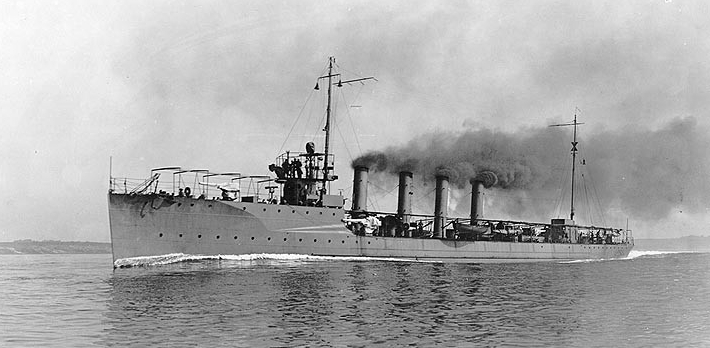
At Whitestone Landing, N.Y., guarding American neutrality, as directed by the Commandant of the New York Navy Yard, Preston, Lt. Cmdr. Cary W. Magruder in command, received a radio message at 2:00 p.m. on 6 April 1917 telling of President Woodrow Wilson signing the declaration of war on Germany. Relieved of neutrality duty by the armed yacht Wasp two days later [8 April], Preston, assigned to Division One, Flotilla One, of the Destroyer Force, got underway at 1:00 p.m. the following day [9 April] and conducted machinery trials in Long Island Sound, upon conclusion of which, at 3:00 p.m., she proceeded to the New York Navy Yard, mooring at 5:20 p.m.
Preston coaled ship at New York on 10 April 1917, and that day received orders directing her to proceed to the Boston Navy Yard and assigning her to the Patrol Force. Underway for Boston on 12 April, she arrived later the same day, mooring alongside Pier No.1. She then escorted Nebraska (Battleship No. 25) to Hampton Roads, Va. (13-15 April), after which she returned to Boston, arriving there on 23 April.
Following a stint on patrol between Cape Sable and Nantucket Shoal (26-30 April 1917), Preston returned to Boston, remaining there until 7:18 a.m. on 4 May, when she stood out in company with Smith (Destroyer No. 17) in accordance with orders [First Squadron Commander’s Campaign Order No. 5 of 3 May 1917] directing them to proceed to Portsmouth, N.H., “scouting the intervening area” while en route and reporting for escort duty to the commanding officer of North Carolina (Armored Cruiser No. 12) upon arrival. The destroyer held target practice at 1:00 p.m. that afternoon, firing 19 shots, then anchored in Portsmouth’s lower harbor at 5:22 p.m. She returned to the Boston Navy Yard for installation of new blowers, the work completed on 4 June 1917, Preston got underway for New York the following day [5 June].
On 14 June 1917, Preston cleared New York as an escort for the first U.S. troop convoy, bound for St. Nazaire, France. One day into the voyage [15 June], seas breaking over the decks amidships washed F1c C. E. Caldicott, F3c J. J. Sullivan, F2c Joseph Hebert, and F3c Lewis A. Williams overboard. As the destroyer prepared to launch a boat to rescue the men, its forward falls carried away, pitching the boat crew into the sea. Although she succeeded in retrieving the would-be rescuers, the four men originally swept over the side drowned. She left the escort on 18 June and returned to New York three days later.
Following repairs at New York (2-5 July 1917), Preston received orders from the Commander, Destroyer Force (Vice Adm. William S. Sims) to proceed to Charleston to prepare for distant service. After arriving at that port she fit out until 22 July when she cleared Charleston for the Azores. After coaling at Bermuda en route, the ship arrived at Ponta Delgada on 31 July and took up anti-submarine patrol and escort duty. A little over a week later, Preston got underway during the mid watch, and stood out of Ponta Delgada at 1:35 a.m., working up to 20 knots, proceeding to the scene of a submarine sighting reported by Prinz Oskar. She joined Reid (Destroyer No. 21) at 9:00 a.m., and took position astern of her. The two destroyers cruised in the vicinity of latitude 35°40'N and longitude 24°15°W from noon to 2:00 p.m. but “saw nothing,” after which they formed up, Reid in the lead, and set course to return to Ponta Delgada. Preston moored at 8:30 p.m. and immediately began a refit.
After refitting, Preston resumed her patrols out of the Azores, and maintained that routine until getting underway on 5 October 1917, for Queenstown [Cobh], Ireland, reaching her destination on 10 October. Following a refit there (11-18 October), during which time she received British depth charges and, on 12 October, a new camouflage design, she cleared Queenstown for the coast of France on 19 October, reaching Brest on 20 October, which she would call home for the remainder of the World War.
While Preston was escorting an outgoing convoy on 21 May 1918, three days out of Brest and en route to New York, the troop transport De Kalb (Id. No. 3010) fired her stern gun to indicate the position of what she believed to be a submarine. Preston immediately went to general quarters and laid a barrage of depth charges astern of the convoy. The crew did not witness any indication of a successful attack. It would be the destroyer’s only recorded scrape with a reported submarine of the war.
The armistice signed on 11 November 1918 ended the World War, and Preston cleared European waters one month later, on 11 December 1918. Five days out, with the barometer falling and strong breezes coming from the southwest, three Sperry depth charges were washed over the side by the sea at 11:15 a.m. Fortunately, the ordnance having had the safety pins inserted prevented their exploding.
While putting in to St. Georges, Bermuda, the homeward bound warship ran aground. She remained fast for five hours but later floated free without serious damage. She arrived at Charleston on 4 January 1919.
Decommissioned on 17 July 1919, Preston was stricken from the Naval Register on 15 September 1919, and sold in the Fourth Naval District to T.A. Scott & Co., Inc., New London, Conn., on 21 November 1919.
S. Matthew Cheser
21 March 2017


